March is Brain Injury Awareness Month
Head trauma is frequently caused by falls, motor vehicle crashes, assaults, sports or combat injuries, and intentional self-harm. All ages may be at risk, especially children, young adults, and those over age 60. Males in any age group are more vulnerable to suffer a brain injury. It is definitively a common medical problem that, at times, goes unattended.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major cause of death and disability in the United States, contributing to about 30 percent of all injury deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).

WHAT IS TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY?
We spoke with Dr. Sushma Lueder of MidAmerica Rehab Hospital in Overland Park, KS., and she shared a bit of insight with us on what exactly TBI is and how to treat it. “If you experience any forceful physical trauma to your head, and it disrupts your brain’s natural functions, then you’ve experienced a traumatic brain injury, or TBI. TBI can occur from an accident as simple as falling off a ladder and hitting your head while doing household chores or as severe as head trauma from a motor vehicle accident, or sports injuries from impact to the head. We treat many of these types of patients and also elderly patients who sustain head trauma from falls due to impaired mobility and balance.”
Doctors classify TBIs as either mild, moderate, or severe. Those who suffer from mild to moderate TBIs tend to recover more fully than those with more severe TBIs. Unfortunately, in those more severe cases, individuals may suffer the effects of damage for a lifetime.
Fortunately, the brain has plasticity. This is what we depend on for any level of TBI recovery. In layman’s terms, plasticity is the brain’s ability to re-wire itself, which leads to recovery. This plasticity is what allows the brain to develop from infancy to adulthood.
WHO IS AT HIGHEST RISK?
According to National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the following are at the highest risk for TBI:
~ Males are approximately 1.5 times as likely as females to sustain a TBI.
~ The age groups at highest risk for TBI are 0 to 4 year olds, 15 to 19 year olds, and adults aged 65 years and older.
~ Certain military duties increase the risk of sustaining a TBI.
~ African-Americans have the highest death rate from TBI.
HOW DOES TBI AFFECT THE BRAIN AND BODY?
“When you have trauma to the brain, the nerves and their neurological pathways are disrupted. If there is bleeding involved, that can cause pressure, leading to neurological disruption,” explains Dr. Lueder. “When a TBI occurs, any brain function is potentially affected. That means your basic body functions, like sleeping, swallowing and bowel and bladder function, can be altered. It also means that the complex parts of your life — your emotions, your thoughts, and your ability to communicate — can also be impaired.”
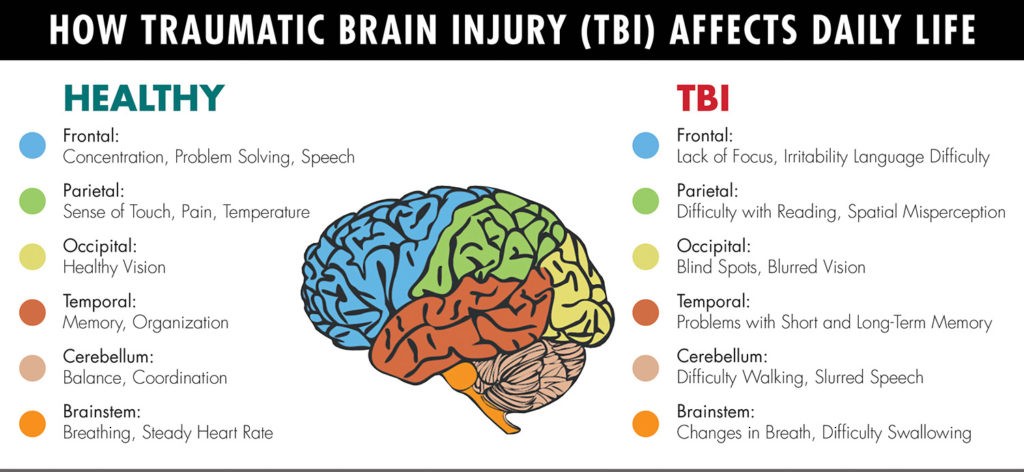
WHAT ARE SOME COMMON OBSTACLES THAT ARISE AFTER A TBI?
“Patients experience difficulties with everyday living, such as getting dressed, bathing and walking. Simple pathfinding, such as getting to a destination point down a hallway can be challenging due to decreased cognitive processing and function,” Dr. Lueder explains. “Options for rehabilitation can be as vast as the conditions that require it. The most important path to follow is the one that best meets the specific needs of patients and that is what’s so great about MidAmerica Rehabilitation Hospital, we are here to help patients navigate those options.”
WHAT ARE SOME LONG-TERM EFFECTS OF TBI?
Because the human brain is so complicated, it’s extremely difficult to predict the long-term effects of any TBI. Most cases of mild TBI will resolve over a course of time with minimal problems. In the case of more serious TBIs, a person can experience any number of changes over the course of months and years.
“Many people with a TBI have problems with basic cognitive skills. It’s difficult for them to pay attention or concentrate, and they might have trouble learning new material. A TBI can also make you think more slowly, or cause you to get easily confused. Even insight — the ability to clearly perceive a situation — can be affected. People with TBI may become impulsive, or develop unusual habits. Things that were once easy — like speaking or brushing your hair — may become difficult or impossible.”
Because the brain regulates our emotional and psychological lives, TBI can substantially alter one’s sense of mental wellness. The TBI might cause a personality change or introduce mental health issues. A person with TBI may have mood swings, depression, irritability, aggression, or disinhibition.
“Healing from TBI takes time. Each individual’s recovery path varies and there is no definite timeline for recovery. When caring for those with a TBI, it is important for the families, patients and healthcare workers involved to have patience. The brain needs time to heal and repair itself,” says Dr. Lueder.
With appropriate help, however, a person with TBI can find ways to cope with these difficulties.
WHY IS IT SO DIFFICULT TO PREDICT THE OUTCOME OF A TBI?
Although the field of neuroscience has advanced our understanding of TBI considerably, we still know a limited amount about the brain’s capacity to heal following injury. Instead of predicting outcomes, rehabilitation professionals often create treatment plans to help people achieve specific goals.
These plans must take into account the severity of injury, the amount of time (if any) spent in a minimally conscious state, and available resources. Neuropsychological evaluations test for areas of specific impairment and can be of great assistance in understanding the severity of injury. Armed with that information, rehabilitation workers can then help people with TBI reach their goals through therapy and other efforts.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES AMONG ALL THE REHABILITATION SPECIALISTS WHO MAY BE NEEDED?
~ Neurologists: Neurologists are doctors who are trained in the diagnosis and treatment of nervous system disorders. These can include diseases of the brain, spinal cord, muscles, and nerves.
~ Physiatrists: Physiatrists are medical experts in rehabilitation medicine. They typically oversee the rehabilitation process.
~ Occupational, Physical, Speech and Language Therapists: These therapists work with a person with TBI to regain cognitive and communication skills, physical abilities, and behavioral skills.
~ Vocational Rehabilitation Experts: These experts are employment coaches who help with regaining job skills.
~ Behavioral Analysts: These specialists create strategies for dealing with behavioral problems.
~ Neuropsychologists: These specialized psychologists focus on thinking skills and behavior problems.
~ Case Managers / Care Coordinators: Case managers / case coordinators assist people in finding and accessing needed programs and services.
Note: Some professionals also carry additional certification from the American Academy for the Certification of Brain Injury Specialists. See: http://www.aacbis.net/ for details.
WHAT ARE SOME OF THE INNOVATIVE TREATMENT PLANS THAT YOU ARE SEEING NOW?
“We have an amazing team at MidAmerica Rehab Hospital – a total of 14 members on our brain injury team. This includes the disciplines of PT, OT, speech therapy, physician, case manager, RN and pharmacist.” Dr. Lueder continues, “By combining the most innovative and advanced technologies with our highly trained team of experts, we ensure that each patient receives the best possible outcome.”
“BITS (Bioness Integrated Therapy System): Our brain injury team finds this to be very useful and helpful to our patients. It challenges and assesses the physical, visual, auditory and cognitive abilities of our patients. Examples of these abilities include reaction time, visual and auditory processing, working memory, physical and cognitive endurance, coordination and visuospatial perception. This tool motivates our patients to improve because they are able to see and track their progress.”
“Bioness: This is an electrical stimulation device that reeducates muscles and reduces spasticity. It is used for the upper extremity to improve hand function and voluntary movement and for the lower extremity to retrain leg muscles and increase motion to improve walking abilities.”
“Vital Stim: This technology electrically stimulates swallow functions and also helps with facial muscle function. Repetitive therapy helps retrain muscle groups for the swallowing process.
There are resources available for traumatic brain injury survivors. The Brain Injury Association of America (BIAA) is a great resource of support for families and individuals living with traumatic brain injury,” Dr Lueder concluded.
For more information on Dr. Sushma Lueder and MidAmerica Rehabilitation Hospital call 913-491-2400 or visit midamericarehabhospital.com